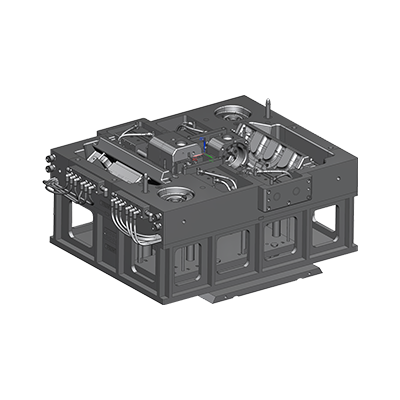
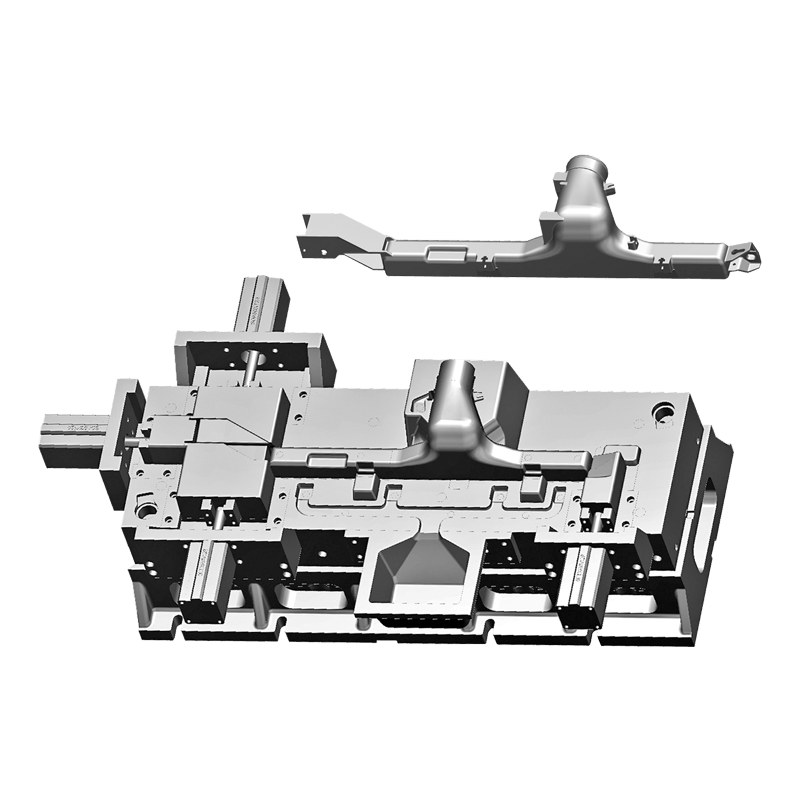
In the design and manufacturing process of cylinder block molds, the design of the cooling system plays a vital role. The cooling system not only has a significant impact on the molding quality of the casting, but is also directly related to the service life and production efficiency of the mold. Reasonable cooling system design can effectively control the temperature changes in the casting process, reduce casting defects, and thus improve the quality of the final product.
The layout of the cooling channel is the core element of the cooling system design. Reasonable cooling channel layout can ensure uniform distribution of the cooling medium and achieve efficient cooling effect. When designing the cooling channel, the following aspects need to be considered comprehensively:
Channel location: The cooling channel should be as close as possible to the heat source area of the casting, especially the key parts of the cylinder block, such as the cylinder wall and cylinder head. This layout can effectively reduce local temperature and avoid deformation and stress concentration caused by excessive temperature.
Channel shape: The shape of the cooling channel should be as simple as possible, avoiding sharp angles and complex bending designs to reduce fluid resistance and ensure the smooth flow of the cooling medium. Such a design helps to improve cooling efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Channel diameter: The diameter of the channel should be reasonably designed according to the flow rate and flow rate of the cooling medium. Too small a channel diameter may lead to too fast a flow rate and increase wear; while too large a diameter will increase the consumption of cooling medium and reduce the overall cooling efficiency. Therefore, accurate diameter design is the key to ensure cooling effect.
The selection of cooling medium also directly affects the cooling effect and production cost. Common cooling media include water, oil and special coolant. When selecting cooling medium, the following factors should be considered:
Thermal conductivity: The better the thermal conductivity of the cooling medium, the more significant its cooling effect. Water has excellent thermal conductivity and is suitable for the cooling needs of most castings.
Corrosiveness: Some cooling media may corrode the mold material, thereby affecting the service life of the mold. Therefore, it is crucial to select a cooling medium that is non-corrosive to the mold material.
Cost and availability: The economy and availability of cooling media are also important considerations in the selection process. Cooling media that are cost-effective and easy to obtain should be given priority to reduce the overall production cost.
Flow control of the cooling system is an important part of ensuring cooling effect. Excessive flow may lead to uneven cooling, while too small flow may not effectively reduce the temperature. To this end, the following measures can be taken:
Flow regulating valve: Install a flow regulating valve in the cooling system to adjust the flow of the cooling medium according to actual needs, thereby ensuring the uniformity of the cooling effect.
Flow monitoring: Monitor the flow of the cooling medium in real time through flow meters and other equipment to ensure that the system always operates in the best working state to achieve the best cooling effect.
Temperature control is also crucial in the cooling system and is directly related to the quality of the casting. Improper temperature control may cause defects such as thermal stress, deformation and cracks in the casting. When designing the cooling system, special attention should be paid to the following points:
Temperature monitoring equipment: Install a temperature sensor in the cooling system to monitor the temperature of the cooling medium in real time to ensure that it remains within a reasonable range.
Temperature control system: Design an automated temperature control system that can automatically adjust the flow and temperature of the cooling medium according to the temperature changes in the actual casting process, thereby ensuring the uniformity of cooling of the casting.


 Pусский
Pусский Español
Español